Using Collektive with Alchemist Simulator
Alchemist Simulator is a distributed systems simulation platform, particularly suited for aggregate programming. It allows you to model and simulate interactions between agents in complex environments, supporting different abstractions and programming paradigms.
Together, Alchemist and Collektive allow you to write aggregate programs in Kotlin that can be executed and simulated within dynamic and configurable environments through YAML files.
In order to use the simulator, you need the following Alchemist dependencies:
dependencies {
implementation("it.unibo.alchemist:alchemist:<latest-version>")
implementation("it.unibo.alchemist:alchemist-swingui:<latest-version>")
implementation("it.unibo.alchemist:alchemist-euclidean-geometry:<latest-version>")
}
And the Collektive incarnation dependency:
dependencies {
implementation("it.unibo.collektive:alchemist-incarnation-collektive:<latest-version>")
}
Note that Alchemist is a JVM only simulator.
YAML configuration file for Collektive
The YAML files define a Collektive simulation run through Alchemist. Below is how it is composed.
Incarnation
incarnation: collektive
incarnation specifies the programming "dialect" used for the simulation. In this case, we use collektive.
Specific configuration
For further details on the configuration options, such as network configuration, node properties and deployment, please refer to the Alchemist documentation.
Program definition
To run a Collektive program within Alchemist,
you need to define the entrypoint of the program in the YAML file.
The action type must be RunCollektiveProgram,
and the parameters must be the fully qualified name of the program to be executed.
_pool: &program
- time-distribution: 1
type: Event
actions:
- type: RunCollektiveProgram
parameters: [it.unibo.collektive.examples.tutorialExample.TutorialExampleKt.maxID]
The program is executed as an Event with a time distribution, in this case, of 1 unit.
The program executed is the function maxID, which is the entrypoint of the program.
Graphical simulation
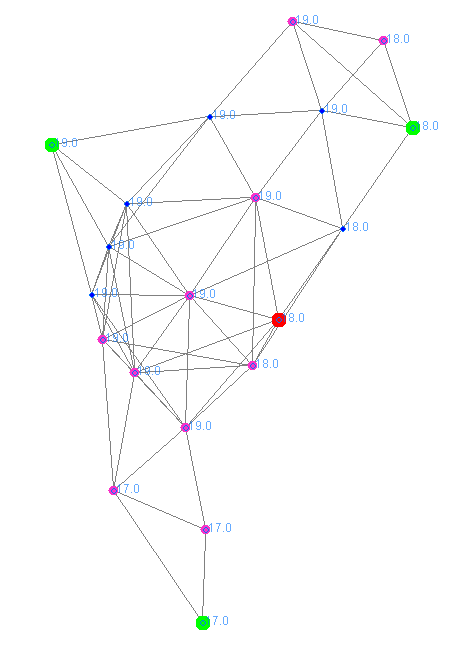
On the left, the network of nodes is displayed with the connection edges hidden, while on the right, the network is shown with the edges between the nodes, from which the interconnection of the network can be observed.
The molecules with Boolean concentration have been used to assign different colors to the nodes based on their role:
- Green nodes are those with the highest ID within a subnet.
- Red nodes are those with the highest ID within their neighborhood, but where a node with a higher ID has been identified within the neighborhood of their neighbors.
- Purple nodes are those located farther from the nearest green node.
- Blue nodes are those that do not fall into any of the previous categories.
- Finally, the labels of the nodes correspond to the maximum ID value identified by each node, allowing for the distinction of three subnets (identified by the ID of the green nodes) and the nodes belonging to each subnet.
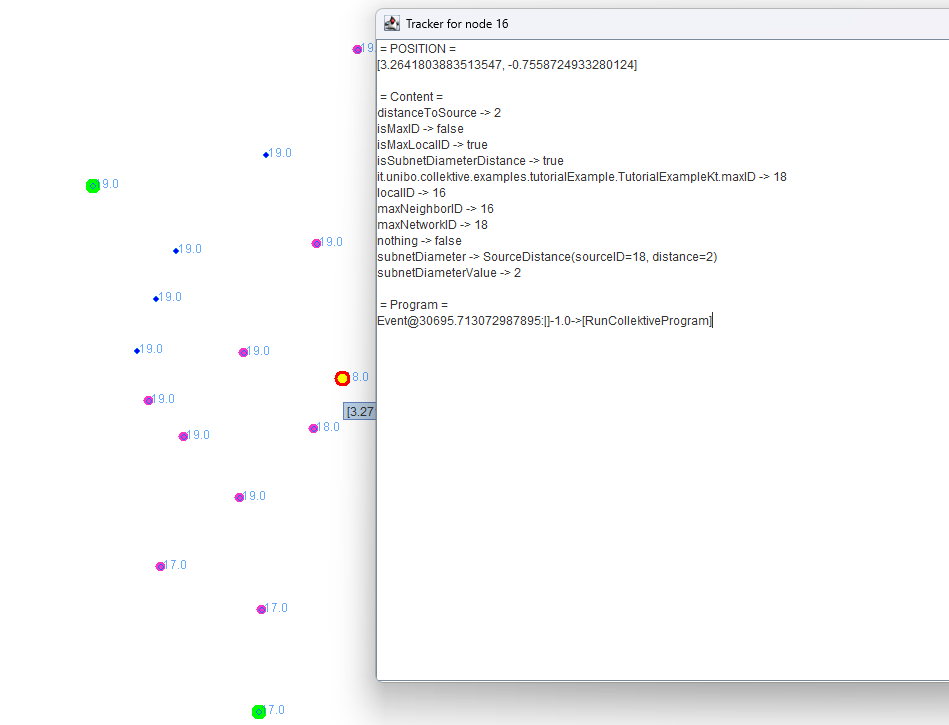
Clicking on a node opens a window displaying the molecule values for the selected node.
Below is presented the example code.
The EnvironmentVariables parameter is used to store and show the values of the molecules within the simulation, it is a node property only related to the Alchemist simulator. A generic Collektive program can and should be written without the need to use the EnvironmentVariables.
fun Aggregate<Int>.maxID(env: EnvironmentVariables): Int {
val maxLocalValue = maxNeighborID()
// Shares the maxNeighborID with neighbors and obtain a field of values
val neighborValues = neighboring(local = maxLocalValue)
// Find the maximum value among neighbors (including self)
val maxID = neighborValues.max(base = maxLocalValue)
// Evaluates the distance from the nearest source
val distToSource = distanceToSource(maxID == localId)
// Calculate subnets diameter
val subnetDiameterValue = subnetDiameter(maxID, distToSource)
val subnetDiameterDistance = subnetDiameter.distance
// Assign the result to the molecules
env["localID"] = localId
env["isMaxLocalID"] = localId == maxLocalValue
env["maxNeighborID"] = maxLocalValue
env["isMaxID"] = localId == maxID
env["maxNetworkID"] = maxID
env["distanceToSource"] = distToSource
env["subnetDiameter"] = subnetDiameterValue
env["subnetDiameterValue"] = subnetDiameterDistance
env["isSubnetDiameterDistance"] = subnetDiameterDistance == env["distanceToSource"]
env["nothing"] = !(env["isSubnetDiameterDistance"] || env["isMaxID"] || env["isMaxLocalID"])
return maxValue
}